Milton Friedman Quantity Theory Of Money. In friedman s modern quantity theory of money the supply of money is independent of demand for money. On the other hand the demand for money is stable.
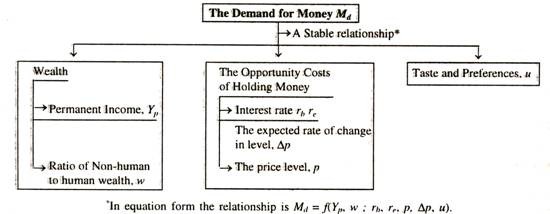
The quantity theory of money takes for granted first that the real quantity rather than the nominal quantity of money is what ultimately matters to holders of money and second that in any given circumstances people wish to hold a fairly definite real quantity of money. On the other hand the demand for money is stable. In friedman s restatement of the quantity theory of money the supply of money is independent of the demand for money.
The theory was originally formulated by polish mathematician nicolaus copernicus in 1517 and was influentially restated by philosophers john locke david hume jean bodin and by economists milton fri.
Due to the actions of the monetary authorities the supply of money changes whereas the demand for money remains more or less stable. For example if the amount of money in an economy doubles qtm predicts that price levels will also double. The supply of money is unstable due to the actions of monetary authorities. The quantity theory of money takes for granted first that the real quantity rather than the nominal quantity of money is what ultimately matters to holders of money and second that in any given circumstances people wish to hold a fairly definite real quantity of money.
